Physical Layer
1. Digital Transmission
2. Transmission Media
3. Guided Media
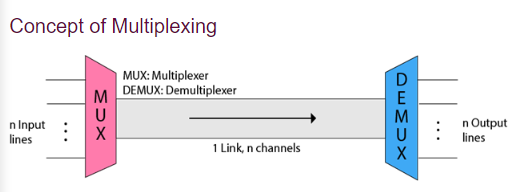
4. Multiplexing
5.Switching
***********************************************
Switching techinique
vvv
**************************************
Multiplexing :- transmission medium is used to send the signal from sender to receiver.
Frequency-division Multiplexing (FDM) :-is a technique in which the available bandwidth of a single transmission medium is subdivided into several channels.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)- optical signals.
Time Division Multiplexing
1. Synchronous TDM :-Synchronous TDM, each device is given some time slot irrespective of the fact that the device contains the data or not.
2. Asynchronous TDM :- technique in which time slots are not fixed as in the case of Synchronous TDM. Time slots are allocated to only those devices which have the data to send.
*************************************
1. Digital Transmission :-
Data Can be represent either analog or digital Form .
1. Digital to Digital Conversion:-
1 Unipolar
2. Polar
3. Bipolar
1. Unipolar : Send Voltage Pulse over the Medium link (Wire or Cable) , in this Voltage represent (1 and 0) so pulse determine whether it Positive or negative. it contain two problem
1. DC component :-
2. Synchronization:-
2. Polar : encoding scheme that uses two voltage levels: one is positive, and another is negative.
*
- NRZ stands for Non-return zero.
- RZ stands for Return to zero.
- Bipolar encoding scheme represents three voltage levels: positive, negative, and zero.
- AMI stands for alternate mark inversion
- B8ZS stands for Bipolar 8-Zero Substitution.
- HDB3 stands for High-Density Bipolar 3.
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION
analog signal is digitalized, this is called an analog-to-digital conversion.
Techniques for Analog-To-Digital Conversion
- PAM stands for pulse amplitude modulation. :-generates a series of digital pulses based on the result of sampling where sampling means measuring the amplitude of a signal at equal intervals.
- PCM stands for Pulse Code Modulation. :- is used to modify the pulses created by PAM to form a digital signal.
Day 2 *****************************************
Transmission Media
1. Twisted Pair :- a. Unshielded Twisted pair 2. Shielded Twisted pair
- Category 1: Category 1 is used for telephone lines that have low-speed data.
- Category 2: It can support upto 4Mbps.
- Category 3: It can support upto 16Mbps.
- Category 4: It can support upto 20Mbps. Therefore, it can be used for long-distance communication.
- Category 5: It can support upto 200Mbps.
Coaxial Cable:-
Coaxial cable is of two types:
- Baseband transmission: It is defined as the process of transmitting a single signal at high speed.
- Broadband transmission: It is defined as the process of transmitting multiple signals simultaneously.
Fibre Optic :-
Core: The optical fibre consists of a narrow strand of glass or plastic known as a core.
Cladding: The concentric layer of glass is known as cladding.
Jacket: The protective coating consisting of plastic is known as a jacket. The main purpose of a jacket is to preserve the fibre strength, absorb shock and extra fibre protection.










No comments:
Post a Comment